
This is critical in helping you select specific data from a worksheet that will be used in a chart.
Therefore, you must first decide what message or idea you wish to present. It is important to keep in mind that the primary purpose of a chart is to present quantitative information to an audience. The first is identifying your idea or message. This is necessary not only to demonstrate the construction of charts but also to explain how to choose the right type of chart given your data and the idea you intend to communicate.īefore we begin, let’s review a few key points you need to consider before creating any chart in Excel.
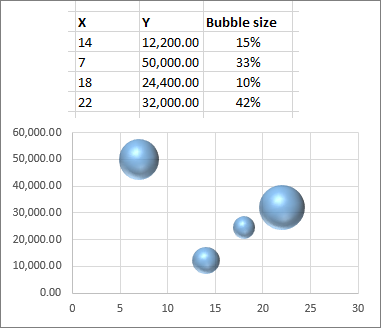
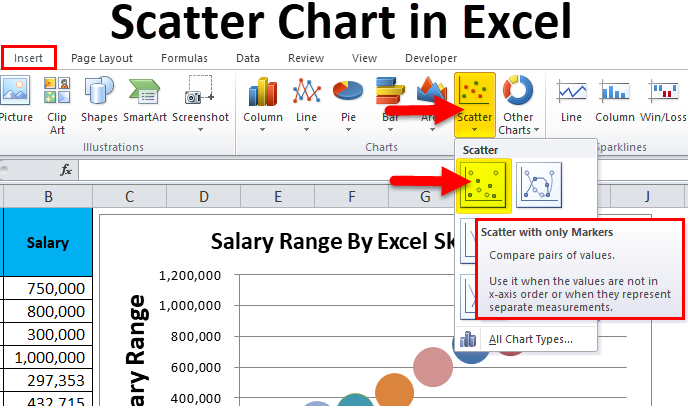
Therefore, instead of addressing a specific theme, we will use a variety of themes. To demonstrate the variety of chart types available in Excel, it is necessary to use a variety of data sets. This section reviews the most commonly used Excel chart types.
In addition, we will examine formatting charts and using those charts in Word and PowerPoint documents. This chapter explores numerous charts that can be used for a variety of purposes. Although there are no rules set in stone for using specific charts for certain data types, some chart types are designed to communicate certain messages better than others. In fact, Excel charts are often imported or pasted into Word documents or PowerPoint slides, which serve this very purpose of communicating ideas to an audience. Your audience can be reading your charts in a written document or listening to you in a live presentation. One of the most important things to consider when using charts in Excel is that they are intended to be used for communicating an idea to an audience. This chapter provides more details for enhancing the appearance of your charts and addresses how to choose the best chart type for your data. Chapter 1 "Fundamental Skills" provided a brief introduction to creating charts in Excel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
